A simple play on Elastic Search
a play with Express Js.
When you go on the popular movie streaming platform Netflix and type “Alchemy of souls“, the movie pops out immediately and when you type “Empress Ki“ or “Playful kiss“, same thing happens and all of sudden you start to notice a change in your movie recommendations, how does that happen? how does Netflix do this instantaneously having 100s of TeraBytes of data to search from?
That’s where Elastic Search comes in. You can read more on how Netflix goes about this here.
Let’s also say that you came up with an idea to build an online academic research repository where you store lots and lots of academic research papers, journals e.t.c from different research institutes and you also need to keep track of user searches so as to provide better journal recommendations based on the search criteria and type of research being done by the user. In a simple use-case of the above scenario, where the data volume isn’t much, using a traditional MYSQL database as a data store is okay, one might even go as far as doing a simple keyword based searching directly on the MYSQL database as is the case here but with a larger dataset and more advanced search requirement , one starts to realize that with the traditional RDBMS full text searching, the search experience becomes poorer, the search starts to produce unpredictable and wrong results, it becomes near impossible to achieve a seamless search experience, in situations like this one is where Elastic Search excels.
One confusion that most people have is that Elastic Search somehow eliminates the need for a primary datastore like a MYSQL database or a PostgreSQL database, the answer is No, Elastic Search is just a search engine that indexes the data in your primary database for near instantaneous searching, it complements the main database and given that it’s built on top of Apache Lucene which lacks data types and constraints, which also does not enforce a schema like in the case of a relational database, Elastic Search is not ideal as a primary datastore. In situations where Elastic Search is made the primary datastore, there’s always a high chance of data loss.
What is Elastic Search?
Elasticsearch is a distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine capable of storing data and searching it in near real time. It is one of the “Search as a Service“ platforms like Azure Search, Prefixbox and Algolia which serves same purpose of indexing and searching data, the major difference between these two industry leaders(Elastic Search and Algolia) comes down to pricing and ease of use, you can find more information about this here.
Elastic Search Use-cases
Use Elastic Search when you are doing a lot of text searching in advanced scenarios where the traditional databases don’t perform really well, where a much more robust searching is a requirement.
Use Elastic Search when log storage and log data visual analysis is a requirement. As in the case of Netflix where user searches are logged and use for making movie recommendations, also in the Research repository scenario.
To continue with this Express Js example:
Create a trial account on Elastic Search using this link.
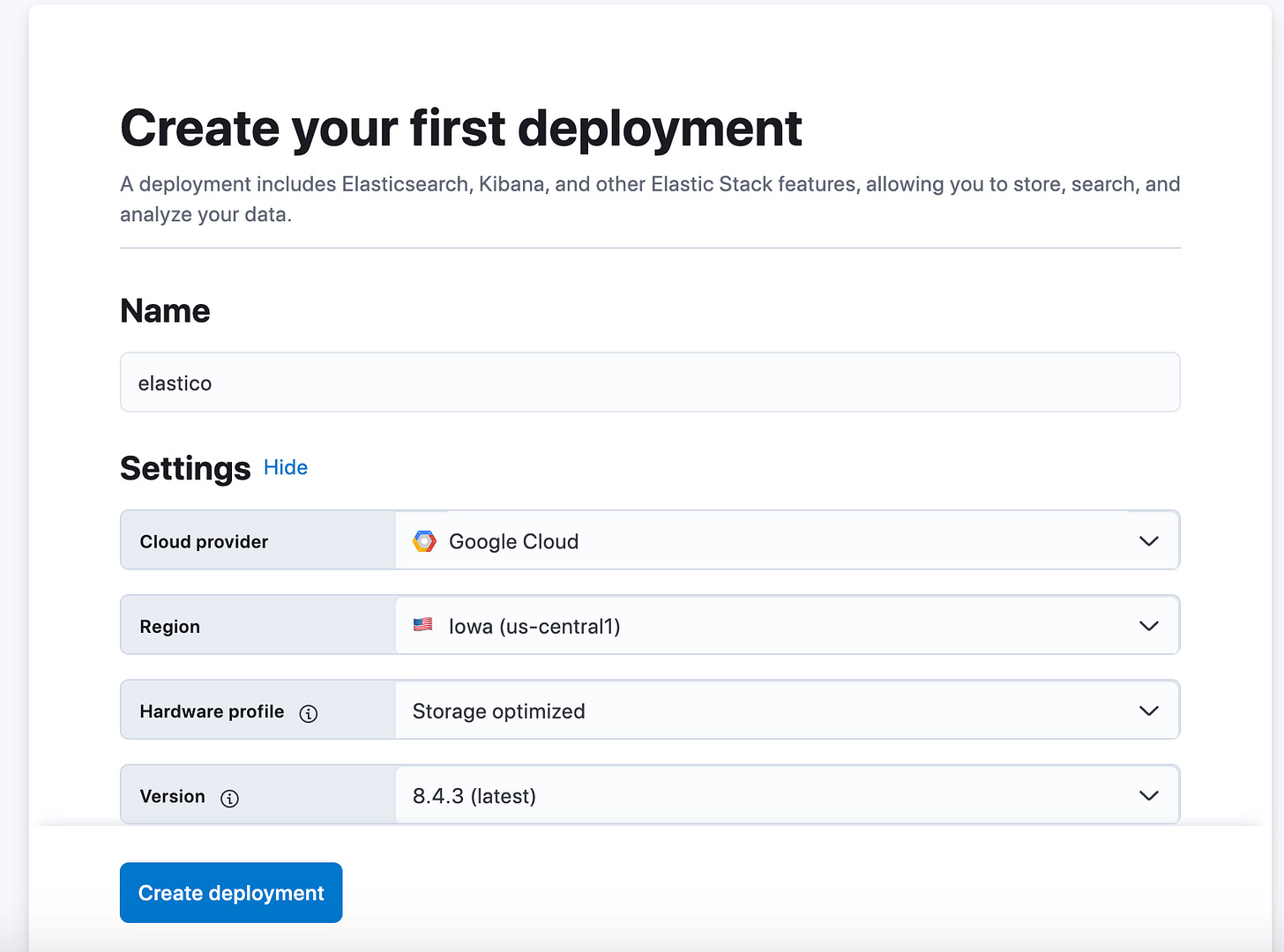
Create a deployment by providing a deployment name e.g. elastico and using the default values for the cloud provider, region, hardware profile and version as shown below
Download the root credentials for super user access of your deployed Elastic Search.
The deployment usually takes about 5 minutes, once done click on continue.
Clone the repository - A-Play-on-ElasticSearch.
Run npm install.
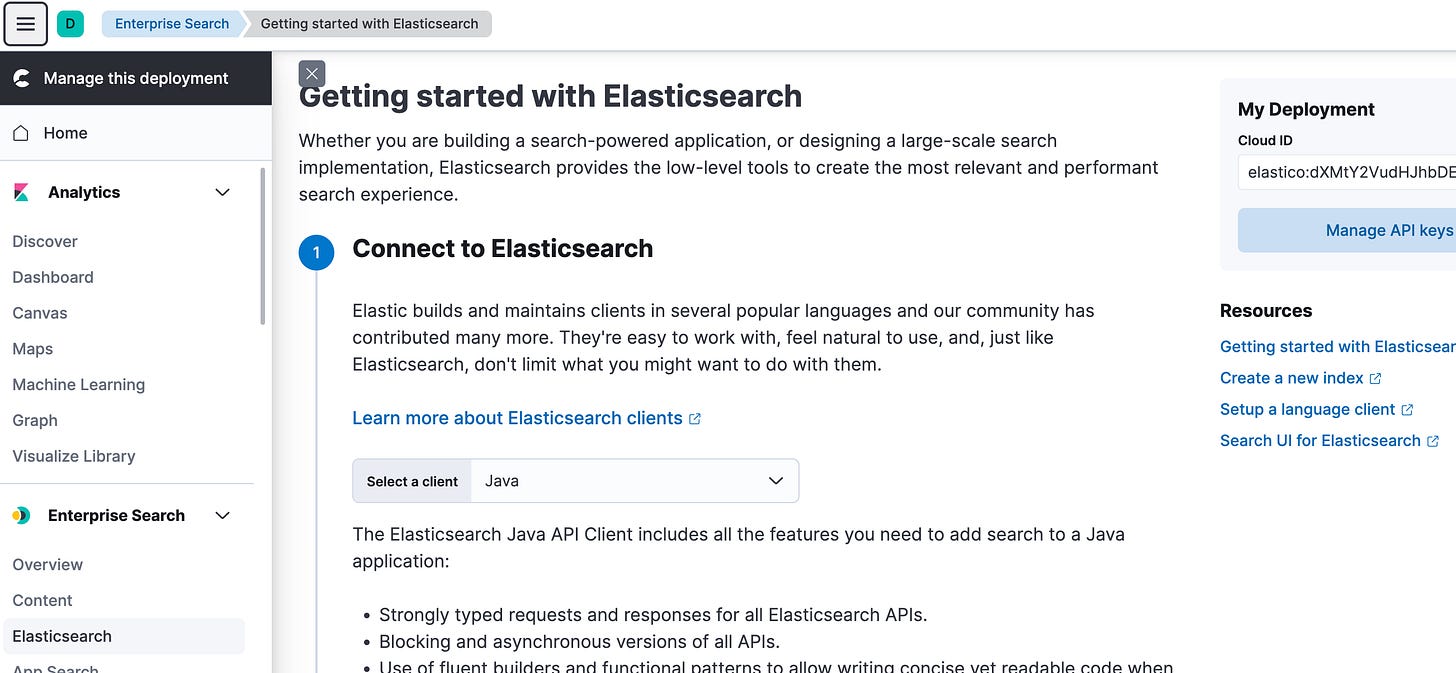
Toggle the sidebar, under Enterprise search, click on Elastic Search
Create an .env file and add
PORT = 3000
CLOUD_ID = your Elastic search cloud Id (copy and paste the cloud ID of your deployment as in the image above).
Click on the light blue Manage API keys button in the above image.
Click on the Create API key, and provide a name for your key
apiKey = your Elastic search apiKey(copy and paster the new api Key here)
Run “npm run index” to index the Game of thrones data in the data folder on Elastic Search.
Start the server by running “npm run dev“
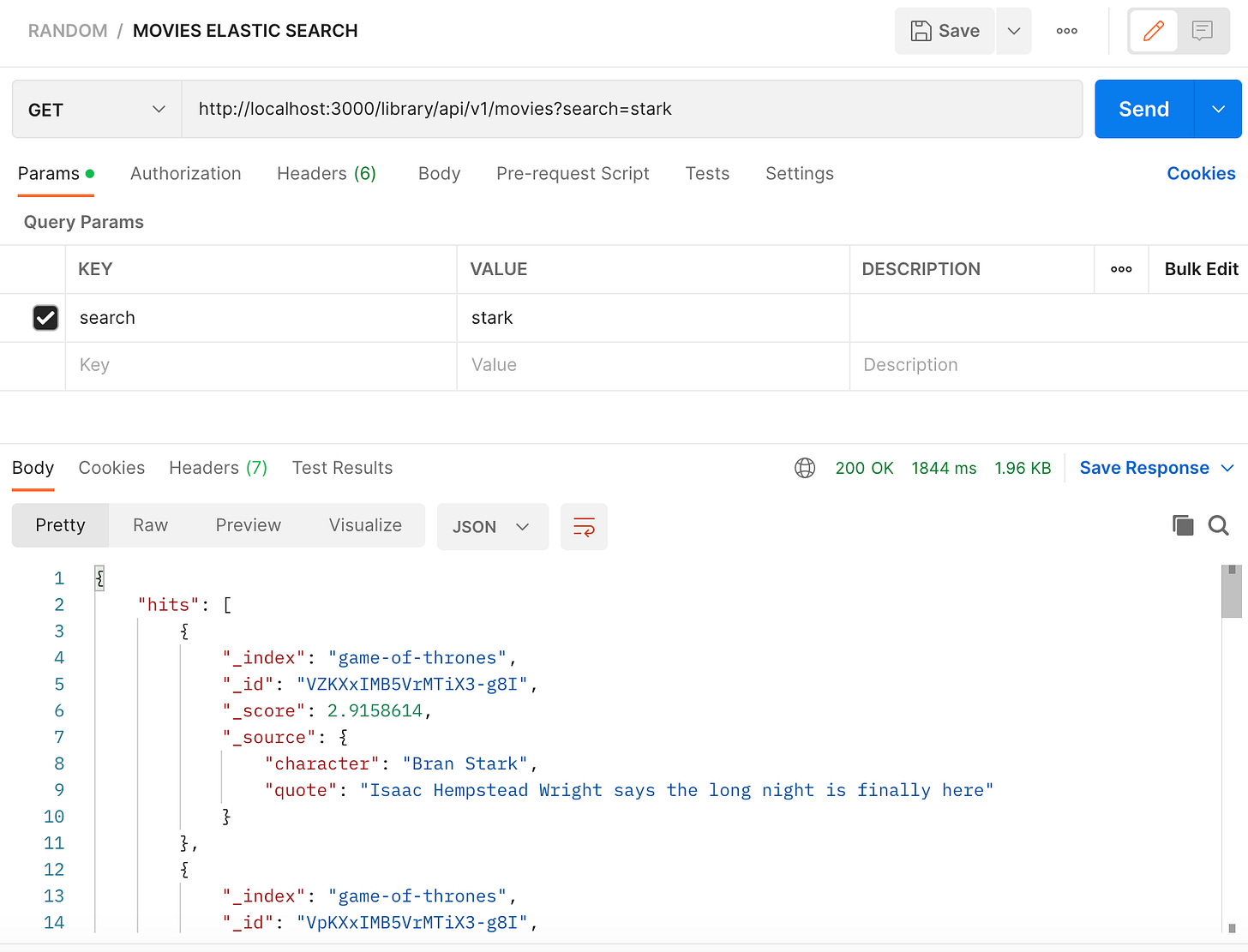
Once your server is started, make a request to the localhost:3000/library/api/v1/movies?search=stark endpoint, you should be able get a response like in the image below
Thank you for reading and I hope this was enough to get you started on the basics of using Elastic Search with Express Js.